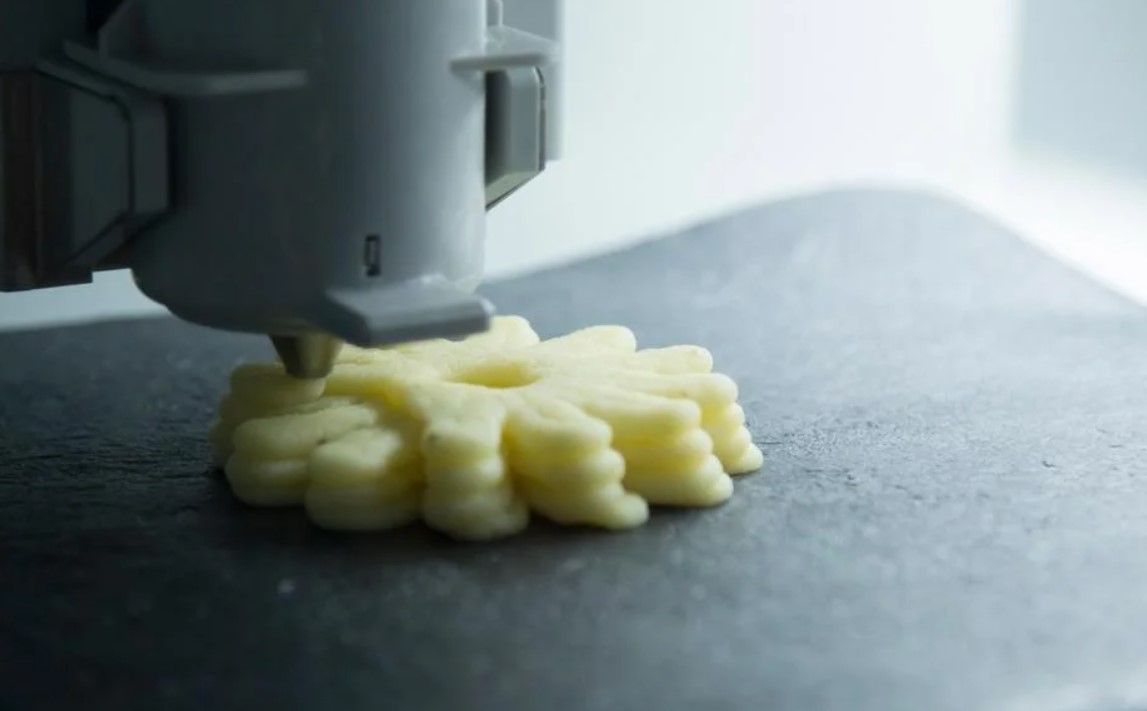
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a technology that creates physical objects from digital models by depositing layers of material on top of each other. 3D printing has been used for various applications, such as prototyping, product development, medical devices, aerospace, and automotive parts. However, in 2023, 3D printing is expected to expand its scope and impact in new and exciting ways. As a 3D printing enthusiast and expert, I have been following the latest trends and innovations in this field for over a decade. I have also personally experimented with different types of 3D printers, materials, and software. In this article, I will share with you some of the trends that will shape the 3D printing industry in 2023.
What are the benefits of 3D printing and why should you care? 3D printing offers advantages such as speed, cost-efficiency, design flexibility, and customization in building structures and components. It can also enable the use of recycled or biodegradable materials, reducing environmental impact. Moreover, 3D printing can facilitate the repair, reuse, and remanufacturing of products, extending their lifespan and reducing waste. Whether you are a hobbyist, a professional, or a business owner, 3D printing can help you create amazing things that were not possible before. Read on to discover some of the most promising trends in 3D printing for 2023.

Consolidation and IPOs in the 3D Printing Market
One of the trends that emerged in 2020 and 2021 was the consolidation and IPOs of 3D printing companies. Several 3D printing companies went public through mergers with special purpose acquisition companies (SPACs), such as Desktop Metal, Markforged, Velo3D, and Shapeways. Other companies, such as Materialize and Stratasys, acquired smaller players to expand their portfolio and market share. These moves indicate that the 3D printing market is maturing and becoming more competitive, as well as attracting more investors and capital.
The consolidation and IPOs of 3D printing companies have several implications for the industry. First, they increase the visibility and credibility of 3D printing as a viable technology for various sectors. Second, they enable the companies to access more resources and scale up their operations, improving their products and services. Third, they create more opportunities for collaboration and innovation among different players in the ecosystem. Fourth, they challenge the existing market leaders to adapt and innovate to maintain their competitive edge.
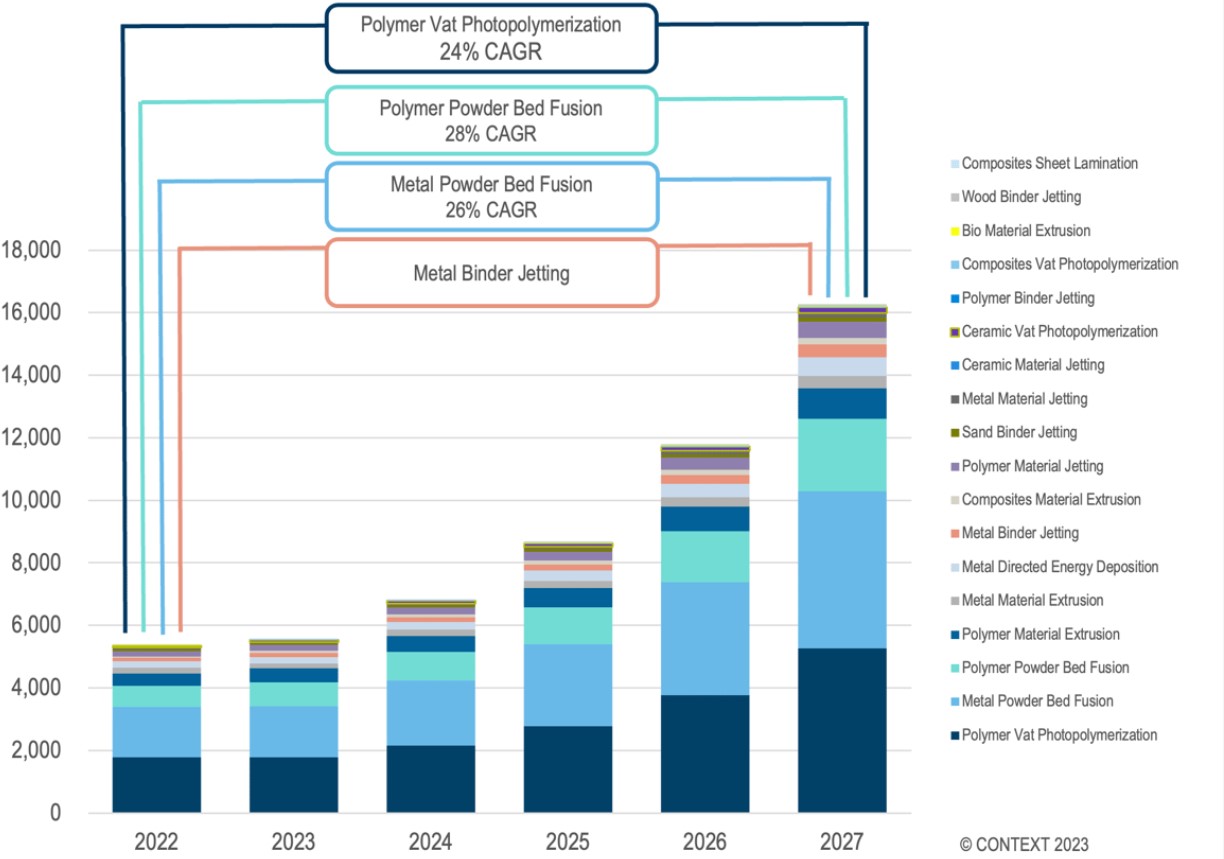
The consolidation and IPOs trend is likely to continue in 2023, as more 3D printing companies seek to capitalize on the growing demand and potential of the technology. According to a report by SmarTech Analysis, the global market for additive manufacturing is expected to reach $51 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15%. The report also identifies some of the key drivers for the market growth, such as metal additive manufacturing, mass customization, digital manufacturing platforms, and sustainability initiatives.
3D Printing in Construction: From Houses to Lunar Bases
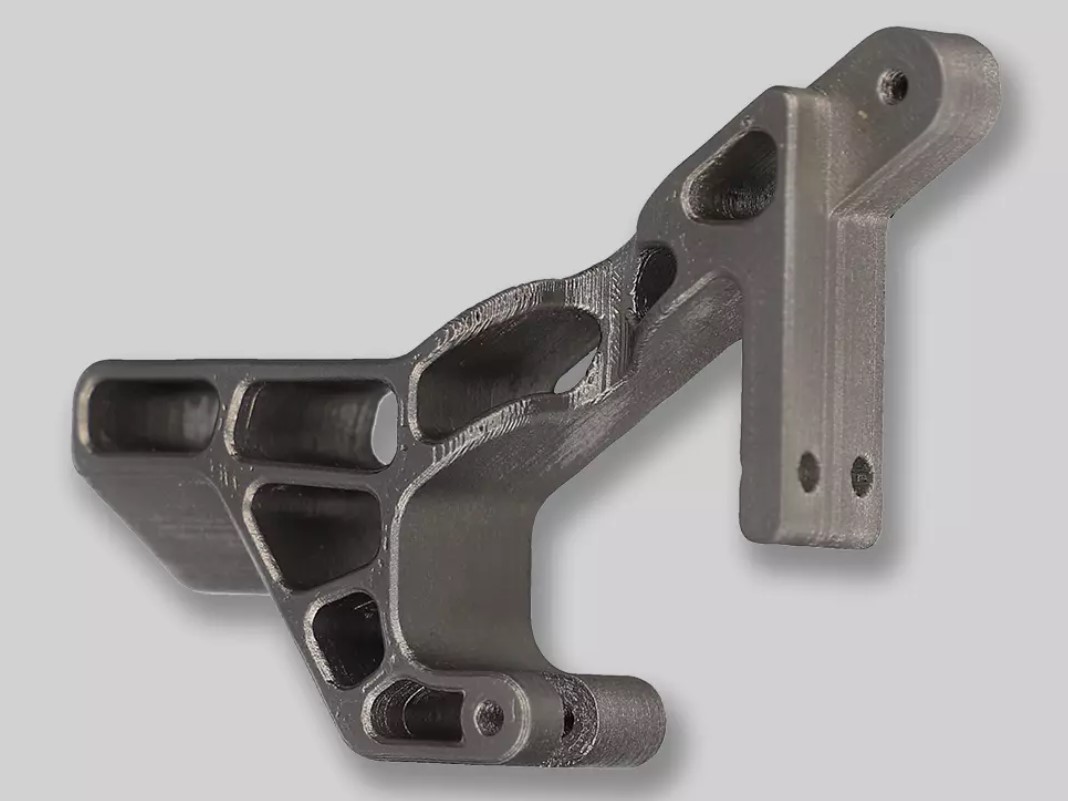
One of the sectors that will see a significant growth of 3D printing in 2023 is construction. 3D printing can offer advantages such as speed, cost-efficiency, design flexibility, and customization in building structures and components. Several projects around the world have demonstrated the potential of 3D printing in construction, such as houses, hotels, bridges, and even a lunar base. Some of the companies that are leading the way in this field are ICON, Apis Cor, COBOD, MX3D, and Relativity Space.
3D Printed Houses
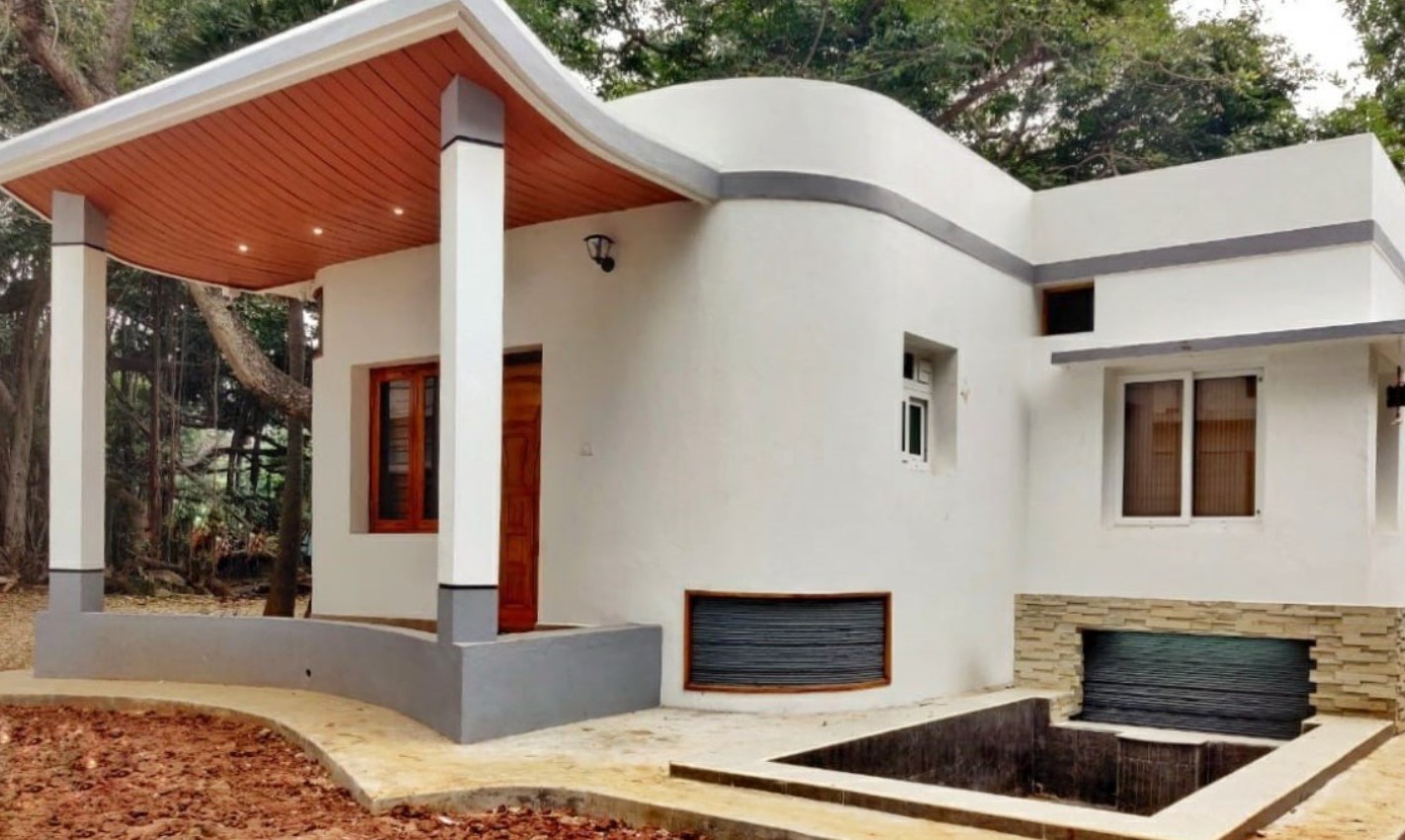

3D printed houses are one of the most common and popular applications of 3D printing in construction. 3D printed houses can be built faster, cheaper, and more sustainably than conventional houses, as they use less material, labor, and energy. 3D printed houses can also be customized to fit different needs, preferences, and environments.
Some examples of 3D printed houses are:
- ICON’s Vulcan II printer, which can print a 1900-square-foot house in less than 24 hours using a proprietary concrete mix. ICON has partnered with New Story, a non-profit organization, to build affordable housing communities in Mexico and Haiti.
- Apis Cor’s mobile printer, which can print a 400-square-foot house in less than a day using a concrete mixture. Apis Cor has printed houses in Russia, Dubai, and the US.
- COBOD’s BOD2 printer, which can print a two-storey house in less than a week using a concrete mixture. COBOD has printed houses in Germany, Belgium, and India.
3D Printed Hotels
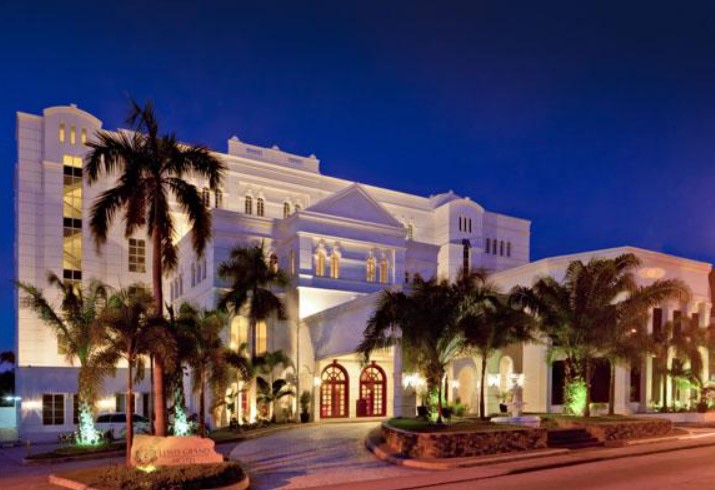

3D printed hotels are another application of 3D printing in construction that aims to provide unique and innovative hospitality experiences. 3D printed hotels can be designed and built with more creativity and flexibility than conventional hotels, as they can create complex shapes and structures that are not possible with traditional methods.
Some examples of 3D printed hotels are:
- The Fibonacci House, a luxury villa in Mexico that was designed by Studio Mortazavi and printed by ICON. The Fibonacci House features a spiral shape inspired by the Fibonacci sequence and has a living area of 500 square meters.
- The Hotel BOD2, a boutique hotel in Copenhagen that was designed by Eentileen Architects and printed by COBOD. The Hotel BOD2 features a modular design that allows for easy expansion and customization.
- The Tecla House, an eco-friendly hotel in Italy that was designed by Mario Cucinella Architects and printed by WASP. The Tecla House features a dome shape made of clay and straw that blends with the natural environment.
3D Printed Bridges
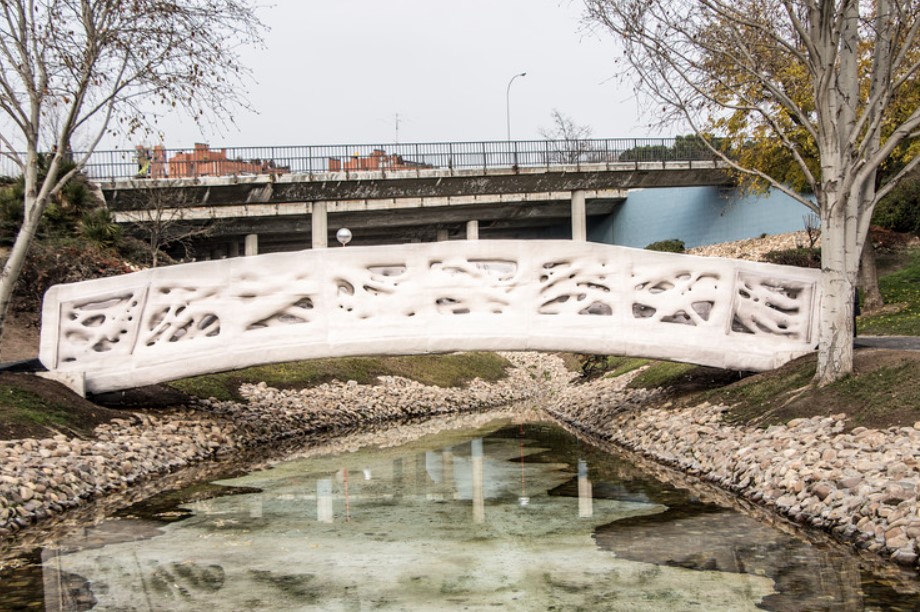

3D printed bridges are another application of 3D printing in construction that showcases the technical and aesthetic capabilities of the technology. 3D printed bridges can be built faster, cheaper, and more safely than conventional bridges, as they use less material, labor, and equipment. 3D printed bridges can also be designed and built with more accuracy and precision than conventional bridges, as they can create complex geometries and structures that are not possible with traditional methods.
Some examples of 3D printed bridges are:
- The MX3D Bridge, a steel bridge that was designed by Joris Laarman Lab and printed by MX3D. The MX3D Bridge features an organic shape that spans over 12 meters across a canal in Amsterdam.
- The Concrete Bridge Project, a concrete bridge that was designed by Zaha Hadid Architects and printed by XtreeE. The Concrete Bridge Project features a parametric design that spans over 30 meters across a river in Shanghai.
- The Striatus Bridge, a concrete bridge that was designed by Block Research Group and Zaha Hadid Architects and printed by Incremental3d. The Striatus Bridge features an arched design that spans over 16 meters across a canal in Venice.
3D Printed Lunar Base
A 3D printed lunar base is one of the most ambitious and futuristic applications of 3D printing in construction. A 3D printed lunar base aims to provide a sustainable and habitable environment for humans on the moon, using local resources such as lunar soil and ice. A 3D printed lunar base can also reduce the cost and risk of transporting materials and equipment from Earth to the moon.
One example of a 3D printed lunar base is:
- Project Olympus, a project that was initiated by NASA and awarded to ICON. Project Olympus aims to develop a robotic construction system that can print lunar habitats using lunar regolith.
Software is an essential component of 3D printing, as it enables the creation, optimization, simulation, and control of digital models and physical prints. In 2023, software advances in 3D printing will include the use of artificial intelligence (AI), digital thread, and cloud computing. AI can help improve the quality, efficiency, and reliability of 3D printing processes by analyzing data, detecting errors, optimizing parameters, and generating designs. Digital thread can help connect the entire lifecycle of a product from design to production to use to disposal by creating a digital record of its history, performance, and status. Cloud computing can help enable remote access, collaboration, scalability, and security of 3D printing operations by storing data and running software on online servers.
Artificial Intelligence in 3D Printing

Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that aims to create machines or systems that can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, and decision making. AI can be applied to various aspects of 3D printing, such as:
- Design: AI can help generate novel and optimal designs for 3D printing by using techniques such as generative design, topology optimization, and neural networks. For example, Autodesk’s Dreamcatcher is a generative design tool that uses AI to explore multiple design options based on user-defined goals and constraints. Another example is Nvidia’s GauGAN, an AI tool that can produce 3D models from text input.
- Process: AI can help monitor and control the 3D printing process by using techniques such as computer vision, machine learning, and feedback loops. For example, Sigma Labs’ PrintRite3D is a process monitoring and quality assurance tool that uses AI to detect defects and anomalies in real time during metal 3D printing. Another example is HP’s SmartStream, a process optimization tool that uses AI to predict and adjust the optimal print parameters for each layer of a multi-jet fusion print.
- Post-Processing: AI can help automate and improve the post-processing steps of 3D printing by using techniques such as image recognition, natural language processing, and robotics. For example, PostProcess Technologies’ AUTOMAT3D is a post-processing platform that uses AI to automate the removal of supports and excess material from 3D printed parts. Another example is AMT’s Digital Manufacturing System, a post-processing platform that uses AI to automate the surface finishing and coloring of 3D printed parts.
Digital Thread in 3D Printing
Digital thread is a concept that refers to the creation and management of a digital representation of a physical product throughout its entire lifecycle. Digital thread can help enhance the traceability, transparency, and efficiency of 3D printing by enabling the integration and communication of data across different stages, systems, and stakeholders. Digital thread can also help ensure the quality, consistency, and security of 3D printed products by enabling the verification and validation of their design, production, and performance.
Some examples of companies that offer digital thread solutions for 3D printing are:
- Link3D, a company that provides a digital manufacturing execution system (MES) that connects the entire additive manufacturing workflow from design to delivery.
- Identify3D, a company that provides a digital supply chain platform that protects the intellectual property and quality of 3D printed products from design to distribution.
- Authentise, a company that provides a data-driven platform that automates the reporting and analysis of 3D printing operations.
Cloud Computing in 3D Printing
Cloud computing is a concept that refers to the delivery of computing services such as storage, processing, software, and networking over the internet. Cloud computing can help enable remote access, collaboration, scalability, and security of 3D printing by allowing users to store data and run software on online servers rather than on local devices. Cloud computing can also help reduce the cost and complexity of 3D printing by providing users with flexible and pay-per-use options.
Some examples of companies that offer cloud computing solutions for 3D printing are:
- Ultimaker, a company that provides a cloud-based platform that allows users to manage multiple 3D printers from anywhere.
- MakerBot, a company that provides a cloud-based platform that allows users to access thousands of ready-to-print models from various sources.
- Onshape, a company that provides a cloud-based platform that allows users to create and edit CAD models collaboratively.